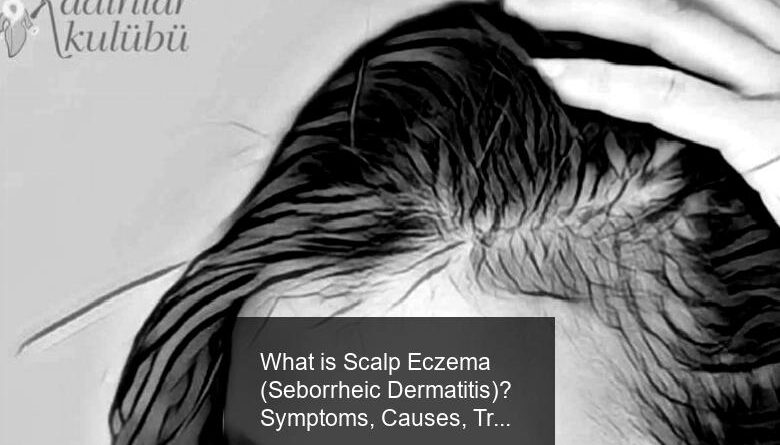
What is Scalp Eczema (Seborrheic Dermatitis)? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Medications
Eczema doesn’t just affect easily visible parts of your body, it can also affect your scalp. In fact, scalp eczema is a type of seborrheic dermatitis eczema that causes inflamed, itchy, dry skin to form on your scalp. The most common type of scalp eczema is known as seborrheic dermatitis, and its most undesirable symptom is dandruff.
It causes scaly patches, red skin and stubborn dandruff. Seborrheic dermatitis can also affect oily areas of the body, such as the face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, and chest.
How Is Eyebrow Dandruff Treated?
Scalp Eczema (Seborrheic Dermatitis) Symptoms
 scalp eczema seborrheic dermatitis symptoms
scalp eczema seborrheic dermatitis symptomsSeborrheic dermatitis signs and symptoms may include:
- Skin scales (dandruff) on your scalp, hair, eyebrows, beard or mustache
- Patches of oily skin covered with scaly white or yellow scales on the scalp, face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, chest, armpits, groin area, or under the breasts
- red skin
- Itching
Signs and symptoms may be more severe if you’re under stress, and they tend to flare up during cold, dry seasons.
Psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis
It often confuses psoriasis and scalp eczema. Having itchy, flaky scalp is a common issue for many people. However, before figuring out how to treat the condition, you must determine its cause. Two conditions that can lead to itchy scalp are psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis:
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease. It can cause skin cells to grow fast enough to accumulate on the skin surface. Patches of rough, scaly skin may appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp.
seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that can cause rough, scaly skin on the scalp and face. The common name for seborrheic dermatitis is dandruff.
How Does Eczema Get Over?
What Are the Causes of Scalp Eczema?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory condition caused by overproduction of sebum, which are natural oils secreted by the sebaceous glands in the scalp. It is not contagious. Because seborrheic dermatitis is a condition of the sebaceous glands, it can also occur in other oily areas of the skin, including the face (eyebrows, eyelids, and middle of the face), ears, upper chest, back, armpits. There is a strong connection between the yeast of the genus Malassezia (fungus), which is normally found on the skin with seborrheic dermatitis, but is often overgrown in people with skin conditions.
Scientists don’t fully understand the exact relationship between yeast and eczema symptoms, but research suggests a nonspecific immune response may be to blame. That is, some interaction between Malassezia, its metabolites (substances produced during metabolism) and the skin and immune cells causes an inflammatory response.
What Are the Triggers and Risk Factors of Scalp Eczema?
 itchy scalp
itchy scalpThere are many triggers that worsen scalp eczema symptoms. In the middle of these triggers are a lot of weather (especially cold, dry air) and tension. Here are some other potential triggers for scalp eczema:
- hormonal changes
- Illness Harsh chemicals from detergents and soaps
- Heavy alcohol use or alcohol-based lotions
- Medicines such as psoralen (for psoriasis), interferon, and lithium
- heavy sweating
- exposure to the allergen
Your risk of developing scalp eczema is increased if you have the following conditions:
- Border system disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, traumatic brain injury, stroke, and epilepsy
- HIV/AIDS
- Other skin conditions such as psoriasis, rosacea, or acne
- allergies
- Asthma
- Obesity
- Depression or eating disorders
The Best Medicines for the Treatment of Eczema on Your Scalp
 If seborrheic eczema is mild, anti-fungal creams, sprays, or ointments are very effective.
If seborrheic eczema is mild, anti-fungal creams, sprays, or ointments are very effective.There is no cure for scalp eczema or seborrheic dermatitis, but medications can help reduce and prevent symptoms. For example, medicated, over-the-counter products often treat irritated and itchy scalp. dandruff shampoo You can treat with The chemical ingredients in these shampoos can help relieve inflammation and get rid of flaky, scaly skin when used two or three times a week. See these items:
- Salicylic acid
- coal tar
- Zinc
- Resorcinol
- ketoconazole
- Selenium sulfide
Topical creams, ointments, or sprays made from these ingredients can also be used to help soothe irritation and stop flaking.
If you have severe scalp eczema, your doctor may prescribe products containing stronger doses of the above-mentioned drugs or products containing other ingredients such as corticosteroids, ciclopirox, sulfacetamide sodium, Protopic (tacrolimus), or Elidel (pimecrolimus).
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis and Is There a Treatment?
How to Prevent Scalp Eczema Burns?
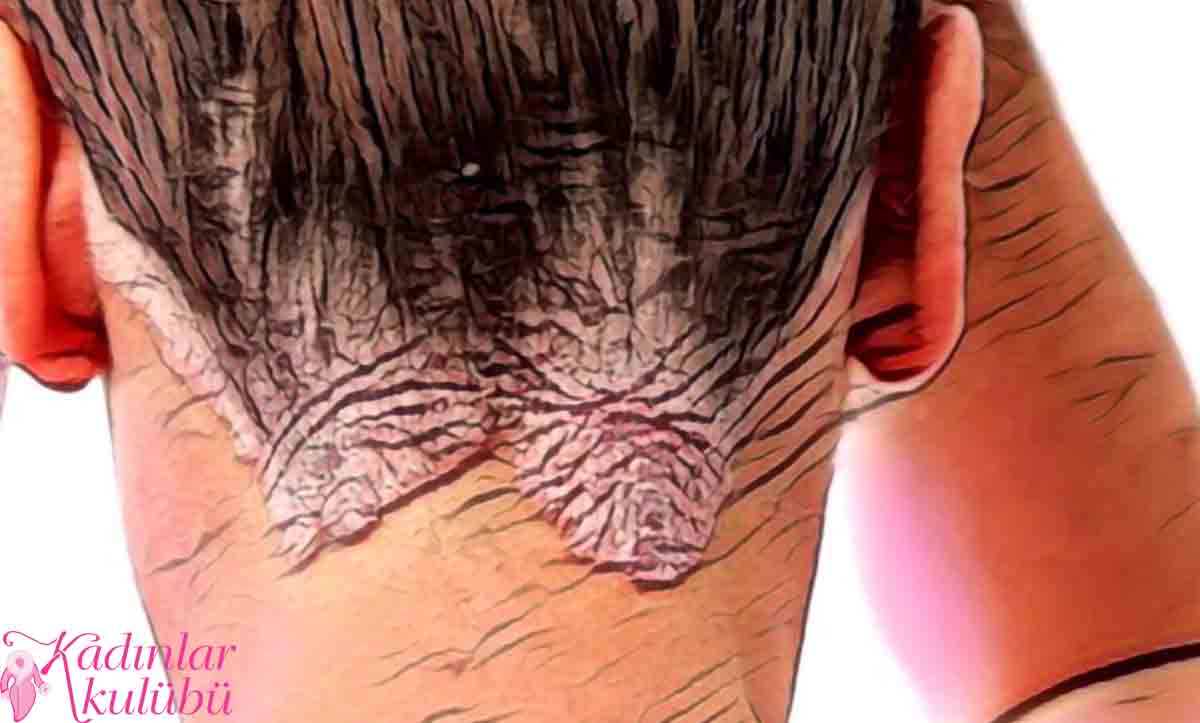
 scalp burn
scalp burnThe severity of seborrheic dermatitis can be reduced by controlling risk factors and triggers and taking care of the skin. Do your best to adhere to the following suggestions to manage scalp eczema and help prevent flare-ups:
- Avoid exposure to suspected irritants and allergens.
- Cleanse your scalp properly, but only use a little shampoo and warm water.
- Manage stress adequately.
- Shampoo your hair after sweating heavily, such as after a workout, as sweating can be a trigger.
Scalp eczema often responds to treatment, but often returns. For some people, sun exposure can improve symptoms.
When scalp eczema becomes extremely severe, physicians prescribe oral antifungal medications for faster relief.
Herbal Remedies for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Scalp eczema can be bothersome, but there are several over-the-counter remedies that can help relieve your symptoms. But as always, consulting an expert can help you control this skin condition. You may want to see a dermatologist and get a prescription treatment to help identify triggers for scalp eczema, especially if the medications you’ve tried aren’t effective or aren’t helping you soothe your scalp eczema.